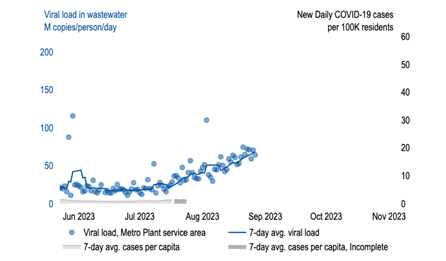
Fall is just around the corner, which generally means an uptick in infectious respiratory diseases, including (yes, again) COVID. One particularly acute example of this is the upward slope of COVID cases, as depicted by the data, below, from the Twin Cities Wastewater study (as discussed in a previous TAG article). Because we would expect this to continue to increase, we see it as a good time to start making preparations to be ready when COVID and other respiratory disease cases rise in your area.
One particular action to take is ensuring you have COVID tests on hand – that are not expired. Test kits are available at drugstores, pharmacies, and some online-direct sites. Although the U.S. government is no longer providing free kits, the Covid.gov website does include links to low- or no-cost testing centers; test kit purchases can be reimbursed by most FSA programs; and some state governments are still providing free kits. Check with your state health department to determine if yours does. For more information on when you should test, how to read the results, and other frequently asked questions, visit FDA’s “At-Home COVID-19 Diagnostic Tests FAQ” webpage.
Earlier this year, FDA also authorized an over-the-counter at-home test that detects both influenza and COVID-19 viruses. The kit holds a single-use at-home test that provides results from self-collected nasal swab samples in about 30 minutes. While it’s not inexpensive, it can be worth the cost for those who have symptoms simulating both viruses and would like to determine if they are positive for Influenza A, Influenza B, or COVID with a single test.
With COVID having reached endemic status, we can expect to be dealing with it, influenza, and other respiratory diseases all at once. And with these viruses having such similar symptoms, testing is an integral part of treatment and renewed health.
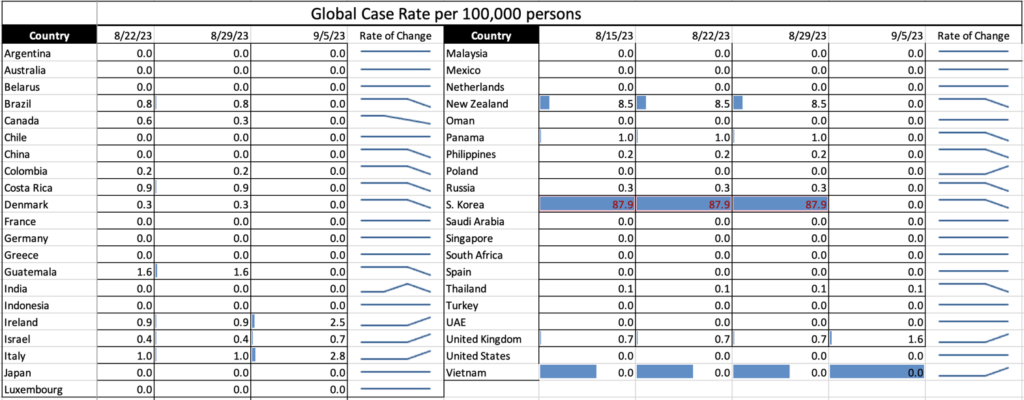
COVID Risk Matrix:
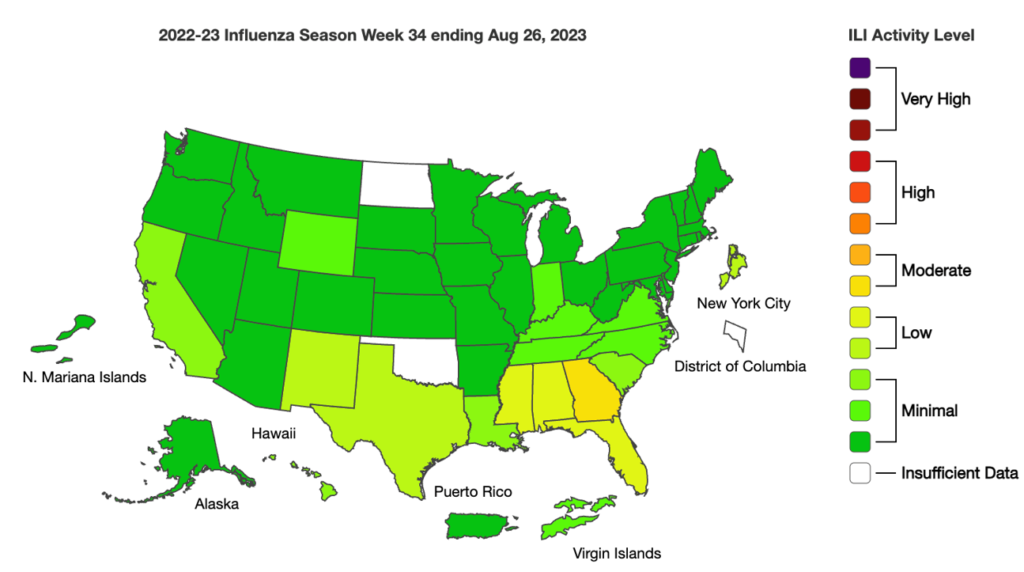
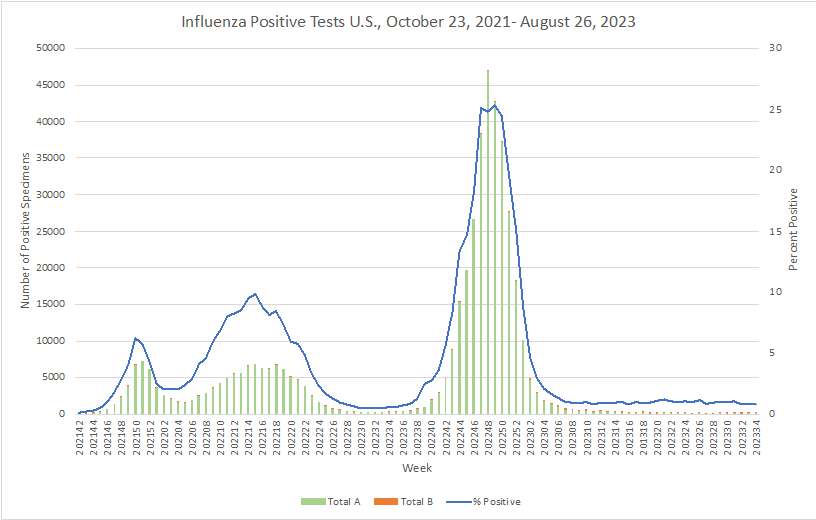
Influenza:
- BA.2.86 COVID-19 strain is circulating and the CDC recently released their initial risk assessment of the variant. The assessment says tests and treatments will likely be effective and that updated vaccines will still be able to reduce severe disease hospitalizations.
- Brain fog from COVID-19 has been linked to blood clots, says a recent study from the UK.
- Rwanda is one of seven countries worldwide that were assessed and selected in 2018 by World Health Organization (WHO) to pilot the validation of viral hepatitis elimination as a public health threat. In their efforts, 7+ million people aged 15 years and older were tested for hepatitis C with 60,000 of them treated, 5 million people were tested for hepatitis B with 7,000 of them on lifelong treatment, and 7+ million people were vaccinated against hepatitis B.
- This summer has seen a sharp increase in the number of laboratory-confirmed influenza cases in Malta, with an average of 21.57 cases being reported weekly during the months of July and August. It is suspected that the higher influx of tourists this year may be contributing to this rise in cases during an atypical period for flu cases in this region.
- An outbreak of Legionnaire’s disease in Rzeszow in southeastern Poland has killed 19 people, health officials said on Sept 2. All those who died also had other illnesses. Around 160 people in the region have been infected with the bacterium that causes the disease, including 107 people in the city of Rzeszow. The proliferation of the bacteria may be linked to the excessive high temperatures the region has experienced.
- Virginia officials are warning residents about a statewide meningococcal disease outbreak which has sickened 27 people since June 2022. Five individuals have died. The illnesses involve Neisseria meningitidis serogroup Y, one of the strains included in the meningococcal conjugate vaccine (MenACWY).