Key Points:
COVID
- In today’s Recommendation for Industry, we discuss the status of COVID, monkeypox and the flu, and the continuing evolution of TAG’s matrices and updates to keep you informed. Read more below.
- Global COVID-19 cases fall 28%; deaths drop 22%. COVID-19 cases fell 28% worldwide last week. This records as the fifth straight week of declining cases. COVID related deaths have dropped 22% from the previous week, reported by the WHO. Global cases have reached 610,149,968, while global COVID deaths today reached 6,519,122, according to the Johns Hopkins tracker. Prevalence of the Omicron BA.5 subvariant increased from 82.4% to 90%, the WHO noted. BA.4 descendant lineages continue to decline, from 8.0% the previous week to 6.1% last week. BA.2 descendant lineages increased slightly again, to 3.2%, but the prevalence of BA.2.75 is still low, at 2.2%. A Stat story today highlights difficulties with vaccine administration errors due to multiple COVID vaccine products in physicians’ offices, pharmacies, and other immunization settings. One such problem is that vaccine vials with the new bivalent (two-strain) options look similar to their monovalent (one-strain) counterparts. Some products need diluting, while others don’t. And immune-compromised people are on a different dosing schedule than those with healthy immune systems. Even before new booster shots were recently approved, more than 5,300 errors in vaccine delivery to children alone were reported, according to CDC data.
- 40% of COVID pneumonia patients still had lung problems at 1 year. As part of a study of adult patients admitted to 12 hospitals in Spain with bilateral COVID-19 pneumonia, researchers analyzed lung function and chest computed tomography (CT) findings 2, 5, and 12 months after hospital release, which was from May 1 to Jul 31, 2020. The findings were published yesterday in Respiratory Research. At 2 months, 53.8% of all patients had impaired lung diffusion, falling to 46.8% at 6 months and 39.8% at 12 months. At 2, 6, and 12 months, 21.5%, 11.3%, and 9.8% of the cohort, respectively, had shortness of breath, and the link between shortness of breath and time since release was significant.
- End of COVID pandemic is ‘in sight’ -WHO chief. The world has never been in a better position to end the COVID-19 pandemic, the head of the World Health Organization said on Wednesday. The WHO is still encouraging countries to take a hard look at their policies and strengthen them for COVID-19 and future viruses. They also urged nations to vaccinate 100% of their high-risk groups and keep testing for the virus. The WHO expects there to be future waves of infections, potentially at different time points throughout the world caused by different subvariants of Omicron or even different variants of concern. U.S. health officials have said that the pandemic is not over, but that new bivalent vaccines mark an important shift in the fight against the virus. They predict that a single annual vaccine akin to the flu shot should provide a high degree of protection and return the country closer to normalcy.
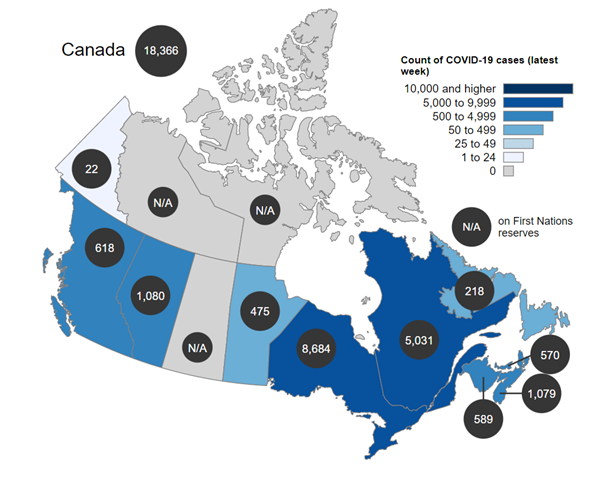
- Canadian case count for the week of August 28 to September 3:
Monkeypox
- CDC head says monkeypox slowing in US. The US continues to have the world’s largest monkeypox outbreak, with 22,630 cases confirmed by the CDC recorded throughout all 50 states. Weekly global cases have declined 3.2% last week, with the most cases reported from the Americas and Europe. The country reporting the highest increase in the past week was Mexico. In the past week 24 countries reported an increase in the weekly number of cases. In contrast, 33 countries have reported no new cases in the past 21 days.
- Two US cases of monkeypox-related brain inflammation raise concern. Two US monkeypox patients developed encephalomyelitis—inflammation of the brain and spinal cord—in the week after symptom onset, one in Colorado and one in Washington, DC, suggesting neurologic complications are a potential outcome of monkeypox infections. The first case of encephalomyelitis was in an immunocompetent gay man in his 30s in Colorado, with no known monkeypox exposure or international travel. According to the authors, 9 days after symptom onset of fever and rash, the patient developed progressive left arm and leg weakness and numbness, urinary retention, and intermittent priapism, and was hospitalized. He was treated with Tpoxx and released with an assistive walking device. The patient in Washington, DC, was also an otherwise healthy gay man in his 30s who similarly had no known monkeypox virus (MPXV) exposure or recent travel. Five days after typical monkeypox symptoms began, he developed bowel and bladder incontinence and progressive flaccid weakness of both legs and was hospitalized. The patient’s condition worsened, and he was intubated and admitted to the intensive care unit. He was treated and released from the hospital with an assistive walking device. Though rare, such outcomes were seen centuries ago during smallpox outbreaks. A severely immunocompromised man died from monkeypox infection in Los Angeles County, officials announced today. This is the first death in the country that has been confirmed due to the virus. The first reported death in Texas is still under investigation.
Food Safety & Public Health
- Patients in outbreak from HelloFresh meal kits spread from Washington to New Jersey. Seven people across six states are sick with E. coli linked to the ground beef in the HelloFresh meal kits. The patients are located in Washington, Pennsylvania, New York, Virginia, Maryland, and New Jersey. Six of the seven individuals have been hospitalized as a result of the bacterial infection. If you have the following food products, throw them away and do not consume them: 10-oz. plastic vacuum-packed packages were distributed in a variety of HelloFresh meal kits. The beef was labeled “GROUND BEEF 85% LEAN/15% FAT”; Packages have “EST.46841” inside the USDA inspection mark and “EST#46841 L1 22 155” or “EST#46841 L5 22 155” on the side of the packaging.
- Ethylene oxide and Salmonella feature in major FSA incidents. The FSA was notified of 2,336 food and feed safety incidents in England, Northern Ireland, and Wales during 2021/22. This is an 18 percent increase compared to 1,978 alerts in 2020/21 but is similar to data in pre-COVID-19 pandemic years. The top four hazard types in 2021/22 were pathogenic microorganisms, allergens, poor and insufficient controls, and pesticide residues. The ethylene oxide issue has been ongoing since September 2020, where it began in sesame seeds from India. There were 129 ethylene oxide incidents in the UK from April 2021 until March 2022. For allergen incidents, root cause analysis data showed labeling verification checks were the top contributor, followed by labeling declaration and procedures not followed. Ingredient cross-contamination, cleanliness or sanitation and ingredient hygiene controls were the main root causes in pathogen incidents. Salmonella dominated while Listeria decreased slightly.
Recommendations for Industry
TAG’s Diseases Matrices and Updates Evolve to Keep You Informed
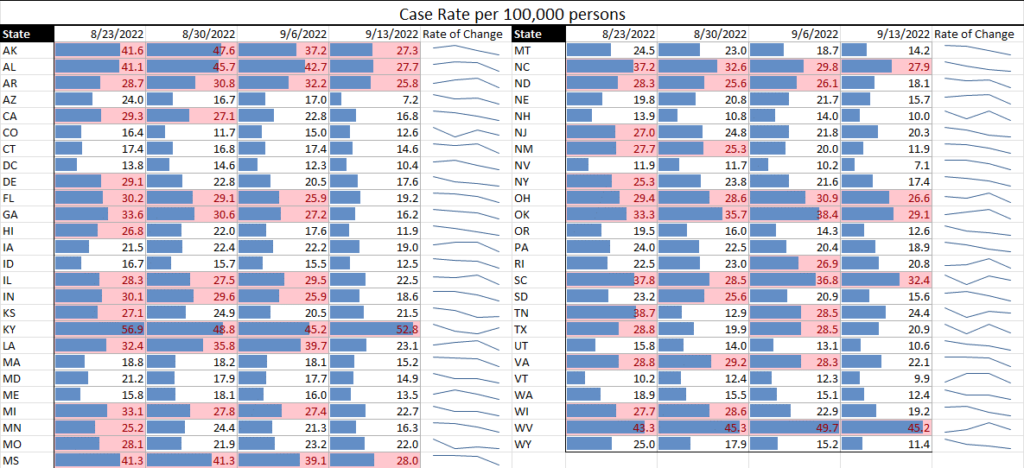
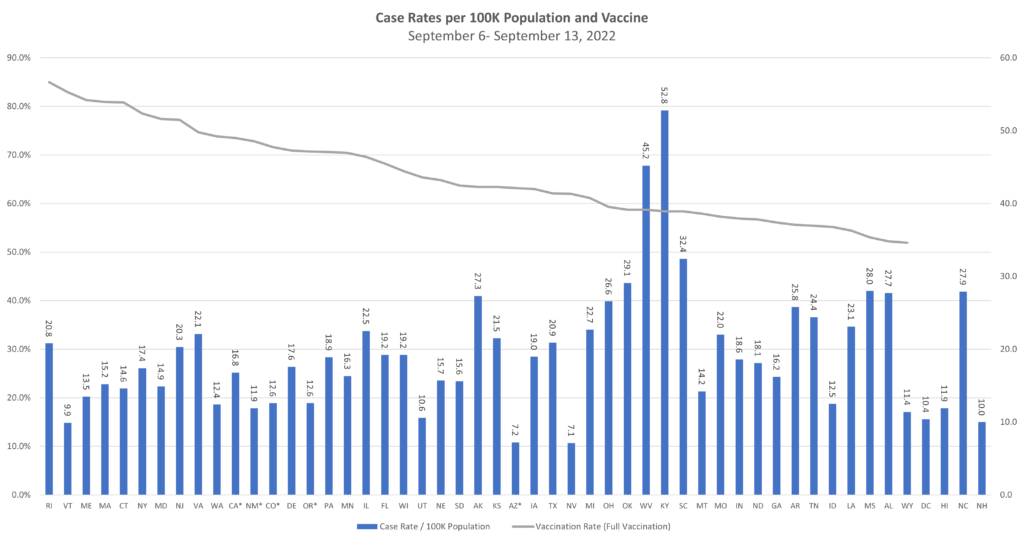
As we continue to see infectious diseases evolving – currently the continuations of COVID and monkeypox, and the gradual seasonal progression of influenza – TAG is making additions and updates to what, for over two years now, has been our weekly matrix update. The weekly graphs will continue to show the COVID case rates and transmissions, will follow monkeypox which is currently in decline, will provide updates on the flu, and will add other evolving infectious diseases as applicable.
For this week: We are seeing both COVID and monkeypox on an overall decline in the U.S., with the list of states at or over a 10% TPR at the shortest it has been in months. Nearly all states are moving downward in effective rates of transmission; hospitalization rates are down; and things are, overall, looking the best they have in months.
Similarly, there are much lower rates of monkeypox, with a dramatic decline being seen in reported cases in the U.S.
We are starting to see cases of influenzas in some states, including Texas, Georgia, New Mexico, and Delaware, though we’re not seeing much yet in other areas. However, we would expect cases to pick up as we move into the cooler weather and people and events move indoors. So, as always, businesses should continue to maintain their wellness programs and ensure employees stay home when ill.
Risk Matrix:
Monkeypox:
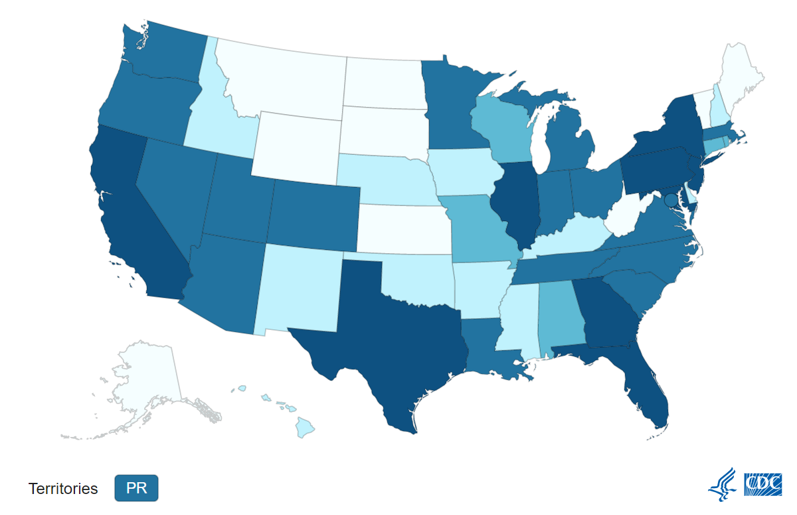

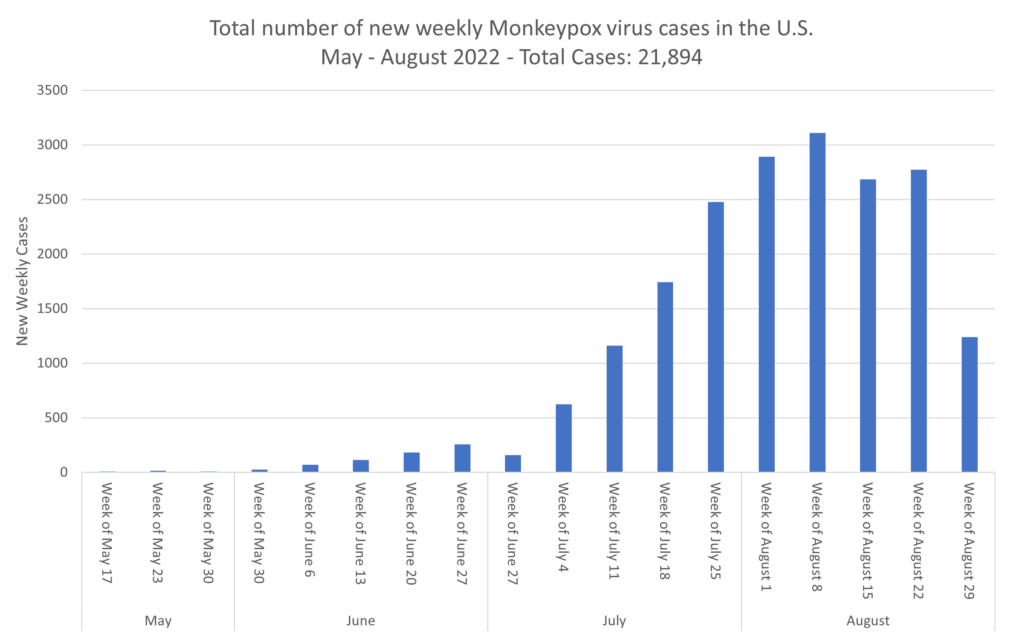
Influenza:
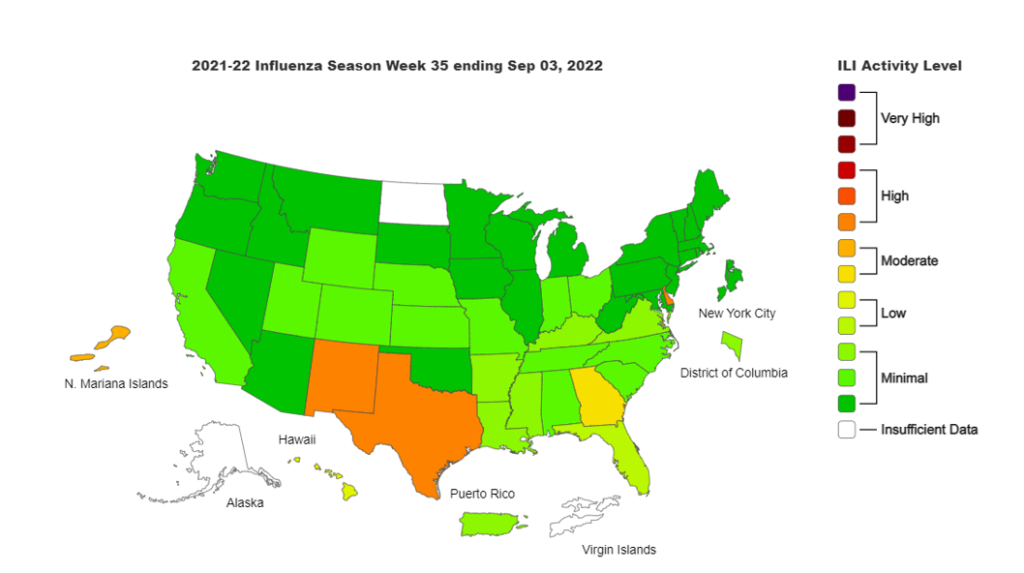
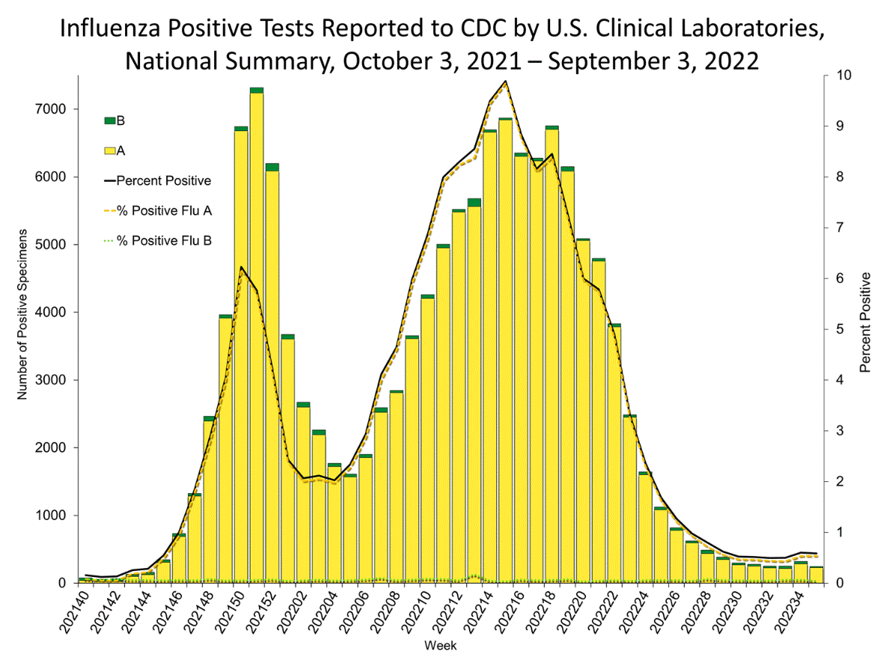
In case you missed it:
COVID
- In Tuesday’s Recommendation for Industry, we discussed what it means to be up to date in COVID vaccinations. Read more here.
- CDC Recommends the First Updated COVID-19 Booster. The CDC is recommending the COVID-19 boosters from Pfizer-BioNTech for people ages 12 years and older and from Moderna for people ages 18 years and older. These updated boosters add Omicron BA.4 and BA.5 spike protein components to the current vaccine composition to restore protection that has waned since previous vaccination by targeting variants that are more transmissible and immune evading. In the coming weeks, CDC also expects to recommend updated COVID-19 boosters for other pediatric groups, per the discussion and evaluation of the data by ACIP on Sept. 1, 2022.
- Study finds Omicron hospital risk 10 times higher in unvaccinated. After the emergence of the Omicron variant, the rate of COVID-19 hospitalizations in the United States was 10.5 times higher in unvaccinated adults and 2.5 times higher in those who were vaccinated but received no booster than in booster recipients, according to a new study. Monthly COVID-19 hospitalization rates were 3.5 to 17.7 times higher in unvaccinated patients than in their vaccinated counterparts, regardless of whether they had received a booster. Hospitalization rates were 10.5 times higher in the unvaccinated and 2.5 times higher in vaccinated patients with no booster than in booster recipients.
- COVID markers decline as US faces uncertain fall. Most US COVID-19 markers continue to indicate slow downward trends, with 7-day averages for cases, hospitalizations, and deaths all decreased from the week before, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) said in its last weekly update. The CDC has urged people getting the updated booster to get vaccinated against flu at the same time. The 7-day average for new daily fatalities dropped 28.1% compared to the previous week, to about 315 a day. As of Sep 7, the 7-day average for new daily COVID-19 cases, at 70,488, has decreased 18.8% compared to the week before.
Monkeypox
- Study raises questions on dose-sparing monkeypox vaccine approach. Dutch researchers published a preprint study done on neutralizing antibodies produced by two subcutaneous doses of Bavarian Nordic’s monkeypox vaccine, Jynneos, and it indicated the dose-sparing strategy might not yield a very strong immune response. Subcutaneous, or intradermal, dosing is being employed in the United States as a way of using one-fifth the usual vaccine dose, thereby allowing many more people to get vaccinated using the same vaccine supply. Officials hoped the strategy would provide the same level of protection as a full Jynneos dose. Researchers most notably pointed out that results show almost no neutralizing antibodies 4 and 8 weeks after vaccination in those who received the first of the advised 0.5-milliliter doses.
- FAQs on Testing for Monkeypox: On September 9, the FDA published a list of frequently asked questions on testing for Monkeypox in order to address the public health emergency. Those can be found here.
- Tpoxx found to be well-tolerated, safe in US monkeypox patients. In Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, researchers from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) provided data on safety outcomes on 369 patients who received the monkeypox antiviral drug tecovirimat (Tpoxx), noting that few adverse events were reported. Of the 369 patients in the study who were administered Tpoxx orally, adverse events were reported in 3.5% of patients, with only one adverse event classified as serious. In Los Angeles County there is an investigation of a death in a monkeypox patient- this is the second case in the US. Globally, the WHO said in a new epidemiologic report that there have been 18 deaths globally.
Food Safety & Public Health
- FDA Announces Targeted Sampling, Additional Efforts to Enhance the Safety of Leafy Greens. Over the last several years, the FDA and partners in the public and private sectors have worked to enhance the safety of leafy greens through the development and implementation of the Leafy Greens STEC Action Plan (LGAP). This work includes prioritized inspections, focused sampling, stakeholder engagement and collaboration, data sharing, root cause investigations, and advancements in the science of detection and prevention. Prevention, Response, and Addressing Knowledge Gaps are the main focuses of this approach as well as accomplishments that have been made since the action plan launched in March 2020- these can be found here.
- FDA announces targeted leafy green sampling in the Salinas Valley. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has announced targeted sampling of leafy greens grown on farms and ranches during the fall 2022 harvest season in the Salinas Valley region of California, releasing results from a 2021 sampling assignment, and providing an update on other work under the action plan. During the fall 2022 harvest season, the FDA plans to collect about 240 lettuce samples from farms and ranches in the Salinas Valley. All samples will be tested for Salmonella spp. and E. Coli O157:H7 and sampling will begin in mid-September and run through October.
- Starbucks Espresso drink recalled over metal fragments in product. PepsiCo Inc is recalling certain Starbucks Vanilla Espresso Triple Shot beverages because of possible contamination by foreign material, specifically metal fragments. The recalled products are in Arkansas, Arizona, Florida, Illinois, Indiana, Oklahoma, and Texas.
- Abbott recalls certain Similac formula over packaging defects. Abbott Nutrition is recalling certain Similac bottles of formula over a packaging defect. This product was distributed in Michigan and Ohio. Specifics on the recalled products can be found here.
- Public alert warns against HelloFresh meal kits linked to new E. Coli outbreak. Federal officials have reported a new outbreak of E. Coli 0157:H7 linked to ground beef in HelloFresh meal kits. No recall is being issued because the product is believed to not be for sale any longer. But the USDA has recommended that if you still have this product at home to throw it away and do not consume it.





